Early symptoms of testicular cancer include a lump in your testicle or testicular swelling, pain, or heaviness. As the condition progresses, you can experience symptoms throughout your body.
The earliest symptoms of testicular cancer can be easy to miss. Unless you’re checking your testicles and scrotum for lumps regularly, you may not notice a small growth in your testicle until it starts to grow and spread.
However, you can look for other symptoms to determine when to seek a diagnosis and treatment.
Read on to learn more about the most common symptoms of testicular cancer, what advanced symptoms to watch out for, and when to contact a doctor.
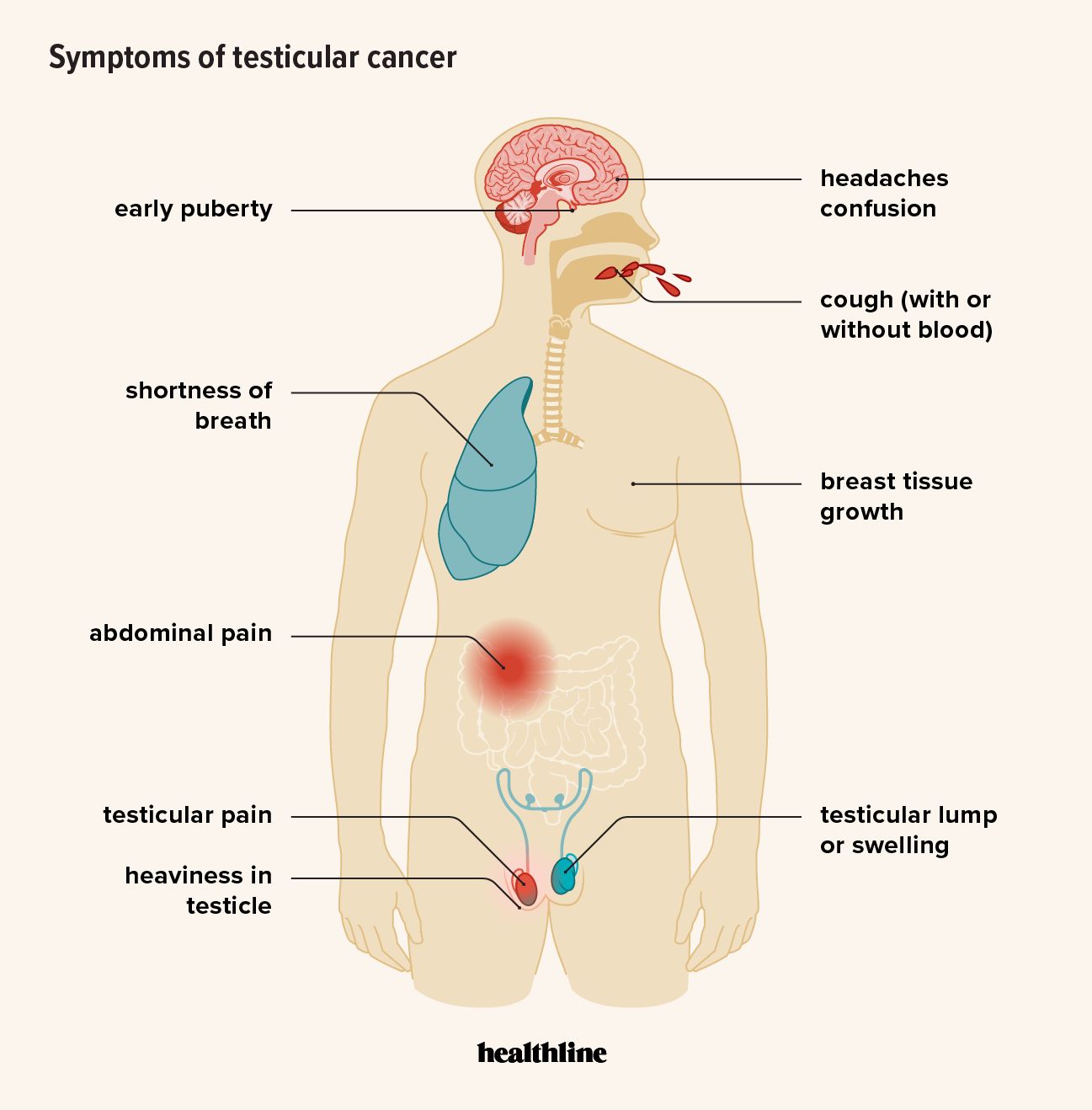
The earliest and most common symptom of testicular cancer is a swollen testicle or lump in your testicle.
A swollen testicle might appear red or cause the skin of the scrotum to look more smooth than usual. This is due to inflammation stretching the usually saggy, wrinkly skin of the scrotum. A swollen testicle might also feel tender or painful to the touch.
A lump in your testicle that lasts for longer than 2 weeks may be a tumor. A lump may not always cause pain or discomfort. But a cancerous tumor can quickly grow and become uncomfortable or start to
Tumors in the testicle can push on tissues and nerves, causing testicle pain or discomfort.
Testicular cancer tumors often grow in the seminiferous tubules — dense networks of ducts in your testicles where you produce sperm. Tumors called
Tumors or cancerous tissue in your testicle can cause a feeling of heaviness or fullness in your testicles.
You might notice heaviness more when you lie down or when you apply pressure to your testicle with tight underwear or pants.
When you experience heaviness in your testicle, you might also notice sharp pains that radiate to your thighs or buttocks.
When testicular cancer starts to grow or spread, it can affect your hormone production or spread through your lymph nodes to other parts of the body, including organs involved in
When there are changes to your hormone production, you might notice that your
Testicular cancer that spreads into the
When testicular cancer spreads beyond your testicles, it can travel through your lymph system. The lymph system is a series of small, connected structures called nodes that support your immune system and filter toxins out of your bodily fluids.
Your lymph nodes are found near every organ in your abdomen, and cancer that spreads to these nodes can cause abdominal pain or swelling.
Tumors that affect
These cells are involved in making
Some advanced symptoms of testicular cancer can include:
- having shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
- losing weight for no reason
- experiencing persistent headache
- feeling confused or disoriented
Contact a doctor if you find a new lump in either one of your testicles and it lasts longer than 2 weeks. Even small lumps can quickly grow and spread.
If you have constant pain and swelling in your testicles that doesn’t go away after a few days, it’s best to seek medical attention.
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about the symptoms of testicular cancer.
What are the warning signs of testicular cancer?
Early signs of testicular cancer can include a lump in your testicle, swelling in your scrotum, or sharp pains in your testicles, thighs, or buttocks. You might also experience a feeling of heaviness in your testicle.
Can you have testicular cancer for years without knowing?
You can have testicular cancer for years without knowing. You might receive a diagnosis during a routine physical exam before you notice any symptoms or lumps in your testicles.
At what age does testicular cancer occur?
In the United States, testicular cancer is most commonly diagnosed among people between
Is testicular cancer fatal?
Testicular cancer isn’t a particularly deadly type of cancer, especially if it’s treated early. The 5-year relative survival rate for testicular cancer is
Looking for symptoms of testicular cancer closely can help you receive prompt diagnosis and treatment.
And the earlier you receive a diagnosis, the lower your risk of long-term complications or death from testicular cancer might be.




